oxaliplatin
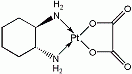 Oxaliplatin (trans-1-diaminocyclohexane oxalatoplatinum) is a platinum-based chemotherapy metallodrug in the same family as cisplatin and carboplatin. Compared to cisplatin the two amine groups are replaced . with 1,2-diaminocyclohexane (DACH) and with an oxalate ligand as a
'leaving group' for improved antitumour activity. A 'leaving group' is an atom or a group of atoms that
is displaced as a stable species taking with it the bonding electrons.
After displacement of the labile oxalate ligand leaving group, active
oxaliplatin derivatives, such as monoaquo and diaquo DACH platinum,
alkylate macromolecules, forming both inter- and intra-strand
platinum-DNA crosslinks, which result in inhibition of DNA replication
and transcription and cell-cycle nonspecific cytotoxicity. The DACH
side chain appears to inhibit alkylating-agent resistance.
Oxaliplatin (trans-1-diaminocyclohexane oxalatoplatinum) is a platinum-based chemotherapy metallodrug in the same family as cisplatin and carboplatin. Compared to cisplatin the two amine groups are replaced . with 1,2-diaminocyclohexane (DACH) and with an oxalate ligand as a
'leaving group' for improved antitumour activity. A 'leaving group' is an atom or a group of atoms that
is displaced as a stable species taking with it the bonding electrons.
After displacement of the labile oxalate ligand leaving group, active
oxaliplatin derivatives, such as monoaquo and diaquo DACH platinum,
alkylate macromolecules, forming both inter- and intra-strand
platinum-DNA crosslinks, which result in inhibition of DNA replication
and transcription and cell-cycle nonspecific cytotoxicity. The DACH
side chain appears to inhibit alkylating-agent resistance.CAS number: 61825-94-3
Chemical formula C8H14N2O4Pt
Molecular weight 397.3
Molecular weight 397.3
The term "oxaliplatin" was found in the following pages: