adenosylcobalamin
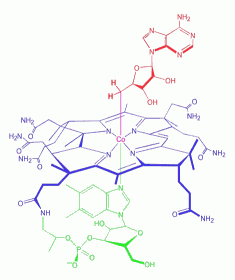 Adenosylcobalamin
is a cobalamin derivative in which the ß-substituent is deoxyadenosyl
(see the red ligand in left figure). It is one of two metabolically
active forms synthesized upon ingestion of vitamin B12 and is the
predominant form in the liver; it acts as a coenzyme in the reaction
catalyzed by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase.
Cobalamins are coenzymatically active forms of vitamin B12
(cyanocobalamin) which is a water-soluble vitamin and a
nutrient essential for all cells. Cobalamin is a
substituted corrin-Co(III) complex (see blue structure in left figure)
in which the cobalt atom is bound to the four nitrogen atoms of the
corrin ring, an axial group R and 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole (DMBI, see
green part in left figure). The latter is linked to the cobalt by the
N-3 nitrogen atom and is bound to the C-1 carbon of a ribose molecule
by the N-1 nitrogen atom. Various forms of the vitamin are known with
different R groups such as R = CN, cyanocobalamin; R = OH,
hydroxocobalamin; R = CH3, methylcobalamin; R = adenosyl, coenzyme B-12
(shown here).
|