Adamsite
Adamsite (DM) is an organoarsenic compound developed near the conclusion of World War I. The chemical warfare compound is solid when pure, and has been used as an aerosol dispersed by thermal grenades or smoke generators. Its effect are: severe irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat. If the agent is inhaled for 1-2 minutes, tightness of the chest and headache are experienced. The headache develops into general nausea, which can result in vomiting in approximately three minutes. Under concentrations expected to occur under combat conditions, fatalities are not expected; however, these compounds can be fatal at higher concentrations.
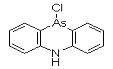 DM was discovered by German scientists in 1913 (Ger. pat. appl. 281049, July 1913 to F. Bayer and Co.), but was never used by Germany. It was independently discovered by Major Robert Adams working at the university of Illinois and also by a British team, both at the beginning of 1918. DM was produced, but not used, by the Americans at the end of the war; Franke states that "according to very incomplete reports [it] was used by the Italian Army." It was produced by many nations for use as a riot control agent until it was superseded by alpha-chloroacetophenone (CN) and similar tear agents. It was also found to be effective as a pesticide against marine borers, which kept in production for years. By 1920, gas mask filters had been improved to protect against aerosol particles, which may account for the termination of this line of development.
Names: DM, 10-Chloro-5,10-dihydrophenarsazine, Adamsite
Molecular formula: C12H9AsClN
CAS Registry Number: 578-94-9
|