Salvarsan
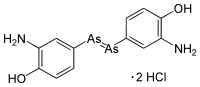 Arsphenamine, also known as Salvarsan and 606, is a drug containing arsenic that was used to treat syphilis and trypanosomiasis. The organoarsenic compound was the first modern chemotherapeutic agent. Arsphenamine was marketed under the trade name Salvarsan in 1910. It was also called 606, because it was the 606th compound synthesized for testing. Salvarsan was the first organic anti-syphillitic, and a great improvement over the inorganic mercury compounds that had been used previously. A more soluble (but slightly less effective) arsenical compound, Neosalvarsan, (neoarsphenamine), became available in 1912. These arsenical compounds came with considerable risk of side effects, and they were supplanted as treatments for syphilis in the 1940s by penicillin. Source: Wikipedia
|