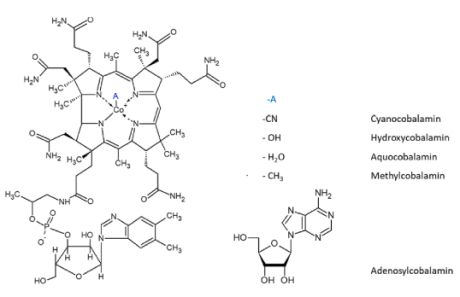
A vitamin synthesized by microorganisms and conserved in
animals in the liver. Deficiency or collective uptake of vitamin B-12
leads to pernicious anemia. It consists of cobalamin, a substituted
corrin-Co(III)
complex in which the cobalt atom is bound to the four nitrogen atoms of
the corrin ring, an axial group A and 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole.
Various forms of the vitamin are known with different A groups such as
A = CN,
cyanocobalamin; R = OH, hydroxocobalamin; R = CH3, methylcobalamin; R =
adenosyl, coenzyme B-12.