|
Glossary
EVISA is providing a list of terms used in the area of speciation and fractionation analysis. Since speciation analysis is a field of analytical chemistry that is specified by a pronounced interdisciplinary cooperation between different sciences such as biochemistry, medicine, biology, environmental sciences, nutritional sciences and material sciences its terminology is a complex mixture of terms used in all these.
You may search for a term or browse the glossary alphabetically.
(In case that you cannot find the term you may consult more special glossaries or handbooks about nomenclature. For more details please consult EVISA's Link pages related to terminology,
|
Also called the oxidation number or oxidation state. An integer (positive, negative, or zero) that describes the number of electrons that must be added or removed from an atom to give it a neutral charge.
|
| |
|
A method which meets or exceeds certain sampling and measurement performance criteria.
  
|
| |
|
|
Action or process of proving that a
procedure, process, system, equipment, or method used works as expected
and achieves the intended results. [CLSI]
|
| |
|
|
The standard deviation squared. If there are
independent sources of errors, the variance of the total error is the
sum of the variances due to the individual sources of error.
|
| |
|
|
Instrument used to sample particles of a given size range according to
their inertia. Particles are removed by impacting them through a
virtual surface into a stagnant volume, or a volume with a slowly
moving airflow, so that large particles remain in this volume while
smaller particles are deflected with the bulk of the original air
flow; the dichotomous impactor is a frequently used virtual
impactor.
|
| |
|
|
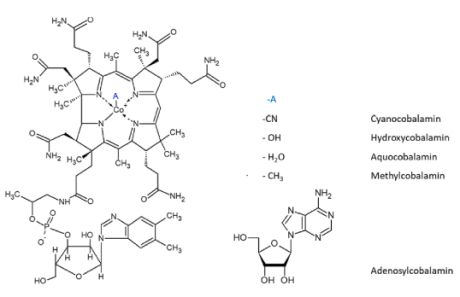
A vitamin synthesized by microorganisms and conserved in
animals in the liver. Deficiency or collective uptake of vitamin B-12
leads to pernicious anemia. It consists of cobalamin, a substituted
corrin-Co(III)
complex in which the cobalt atom is bound to the four nitrogen atoms of
the corrin ring, an axial group A and 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole.
Various forms of the vitamin are known with different A groups such as
A = CN,
cyanocobalamin; R = OH, hydroxocobalamin; R = CH3, methylcobalamin; R =
adenosyl, coenzyme B-12.
|
| |
|
|
readily evaporates at room temperature.
|
| |
|
|
species occurring as gas or vapor by application of heat, by reducing pressure, by chemical reaction of by a combination of these procedures; example: arsin
|
| |
|
|
Voltammetry is a common name for a large group of
instrumental techniques which are based on measuring the electric
current formed by a continuous potential shifting on the electrodes.
The potential of the working electrode is controlled (typically with a
potentiostat) and the current flowing through the electrode is
measured. In one of the most common applications of the technique, the
potential is scanned linearly in time; this is called the "linear-sweep
voltammetry," "LSV," or "LV." "Cyclic voltammetry (CV)" is a
linear-sweep voltammetry with the scan continued in the reverse
direction at the end of the first scan, this cycle can be repeated a
number of times.
This electrochemical measuring technique can
be used for the determination of the kinetics and mechanism of electrode reactions (redox reactions of extremely small
amounts of chemicals) and for electrochemical analysis used to quantify the involved species.
|
| |
|