diphenylarsinous cyanide
Diphenylarsinous cyanide (DC) is an organoarsenic compound developed near the conclusion of World War I. The chemical warfare compound is solid when pure, and has been used as an aerosol dispersed by thermal grenades or smoke generators. Its effect are: severe irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat. If the agent is inhaled for 1-2 minutes, tightness of the chest and headache are experienced. The headache develops into general nausea, which can result in vomiting in approximately three minutes. Under concentrations expected to occur under combat conditions, fatalities are not expected; however, these compounds can be fatal at higher concentrations.
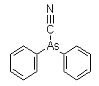 DC was used by the Germans in 1918. It was intended to combine the vomiting potential of DA with the lethality of cyanide. However, DC did not prove particularly lethal in tests. DC was a standard agent (Red No. 1) in the arsenal of the Japanese Imperial Forces between 1931 and 1945.
Names: DC, Diphenylarsinous cyanide, Clark II, diphenylcyanoarsine
Molecular formula: C13H10AsN
CAS Registry Number: 23525-22-6
|