The quality of data generated by speciation analysis is especially critical whenever decisions based upon the amounts of species are related to human health risks. The quality and validation of these measurements using the approved analytical methodology could be significantly enhanced by incorporating certified reference materials as part of the quality control protocols, yet this has not been widely implemented. Here, we briefly discuss how data from certified reference materials can provide critical information that can impact assessments regarding data use that is unavailable by other means.
Quality controlAnalytical chemistry is a science providing information about the composition of matter collected under a special situation, meant to be a sample representing a case or situation. The analysis should provide information that is useful and reliable and is suitable for achieving some requested end purpose in an efficient, timely, and cost-effective manner. Tools of quality assurance and control are meant to ensure that valid analytical results will be produced by using a certain analytical method with proper instrumentation. Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) are an integral part of these QA/QC tools.
Two types of CRMs are provided by the CRM producers: those intended for use in calibrating measurement systems and those primarily intended to help validate the performance of measurement systems. Figure 1 shows how these two types of materials fit within the complete measurement process, connecting the measurements to the International System of Units (SI).
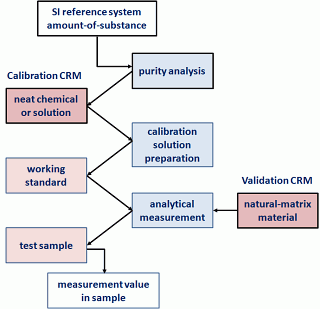
Figure 1: Uses of an CRM
The boxes to the left and right in Figure 1
represent materials, those in the centre represent activities, and the
arrows indicate the flow of the complete measurement process from the SI
reference system to the desired measurement value. The boxes and lines
in black denote the materials and activities provided by the CRM
producer. The boxes and lines in blue denote the materials and
activities that you must provide.
|
A calibration CRM is typically either a “neat” material of established high purity or a simple solution gravimetrically prepared from a material of established high purity. Such materials are used to establish the relationship between the quantity of a measurand (e.g. concentration) and the results from a measurement process (signal).
Validation/verification materials are typically preparations of naturally occurring materials of a comparable matrix as the unknown samples that a) contain desired levels of the analytes of interest, b) have been processed to have uniform composition, and c) may have been modified for improved stability. When developing an analytical method, these materials are used to evaluate whether the calibration relationship established for a measurement process is valid when analysing a particular sample matrix. When implementing a method in a given situation (particular equipment, reagents, analysts, etc.), these materials are used to verify that the developed measurement process indeed provides the expected results.
Metrological traceability to the SI can then be established through the calibration of the measurement system with a certified calibration material, followed by validation of the measurement process with the appropriate natural-matrix CRM. When neither certified calibration solutions nor neat materials are available, traceability can be established by calibrating with a natural-matrix material. However, by definition, the traceability chain for natural-matrix materials has at least one more link than that of a calibration material and so will not provide the smallest possible measurement uncertainty. As a rule of thumb, assigned uncertainties for the CRM should not be greater than one-third of the target uncertainty for the analysis of samples.
Selection of an appropriate CRM
The value resulting from the use of the CRM for validation purpose depends on the similarity between the CRM and the sample to be analysed, with respect to matrix and analyte composition. Since interference effects might be concentration dependent, also concentrations should lie within the same general range on the calibration curve. Unfortunately, because of the limited number of CRMs available, such ideal selection can only seldomly be realized.
The use of CRMs for method evaluation with respect to reproducibility of measurements is a misuse of the costly material, since such measurements can be performed on any homogenous, stable material available in sufficient quantity having an appropriate matrix and analyte content.
 Related EVISA Resources:
Related EVISA Resources:
 Brief summary: Speciation Analysis - Striving for Quality
Brief summary: Speciation Analysis - Striving for Quality Brief summary: Certified Reference Materials for Speciation Analysis
Brief summary: Certified Reference Materials for Speciation Analysis Brief summary: Certified reference materials for mercury in marine animal tissues
Brief summary: Certified reference materials for mercury in marine animal tissues Brief summary: Simple certified reference materials for speciation analysis
Brief summary: Simple certified reference materials for speciation analysis  Brief summary: Certified reference materials for arsenic species in biological materials
Brief summary: Certified reference materials for arsenic species in biological materials  Brief summary: Certified reference materials for arsenic in marine animal tissues
Brief summary: Certified reference materials for arsenic in marine animal tissues Brief summary: Organotin compounds in marine organisms
Brief summary: Organotin compounds in marine organisms
 Brief summary: CRMs for the speciation analysis of chromium in environmental materials
Brief summary: CRMs for the speciation analysis of chromium in environmental materials Brief summary: Certified reference materials for selenium speciation
Brief summary: Certified reference materials for selenium speciation Brief summary: Certified reference materials for lead speciation
Brief summary: Certified reference materials for lead speciation Brief summary: Chemical speciation analysis for nutrition and food science
Brief summary: Chemical speciation analysis for nutrition and food science Link page: All about CRMs
Link page: All about CRMs
 Link page: All about food science
Link page: All about food science
 Link page: All about quality of measurements
Link page: All about quality of measurements
 Material Database: CRMs for speciation analysis
Material Database: CRMs for speciation analysis
last time modified: September 24, 2024